Before starting, lets visualize a illustration how it works
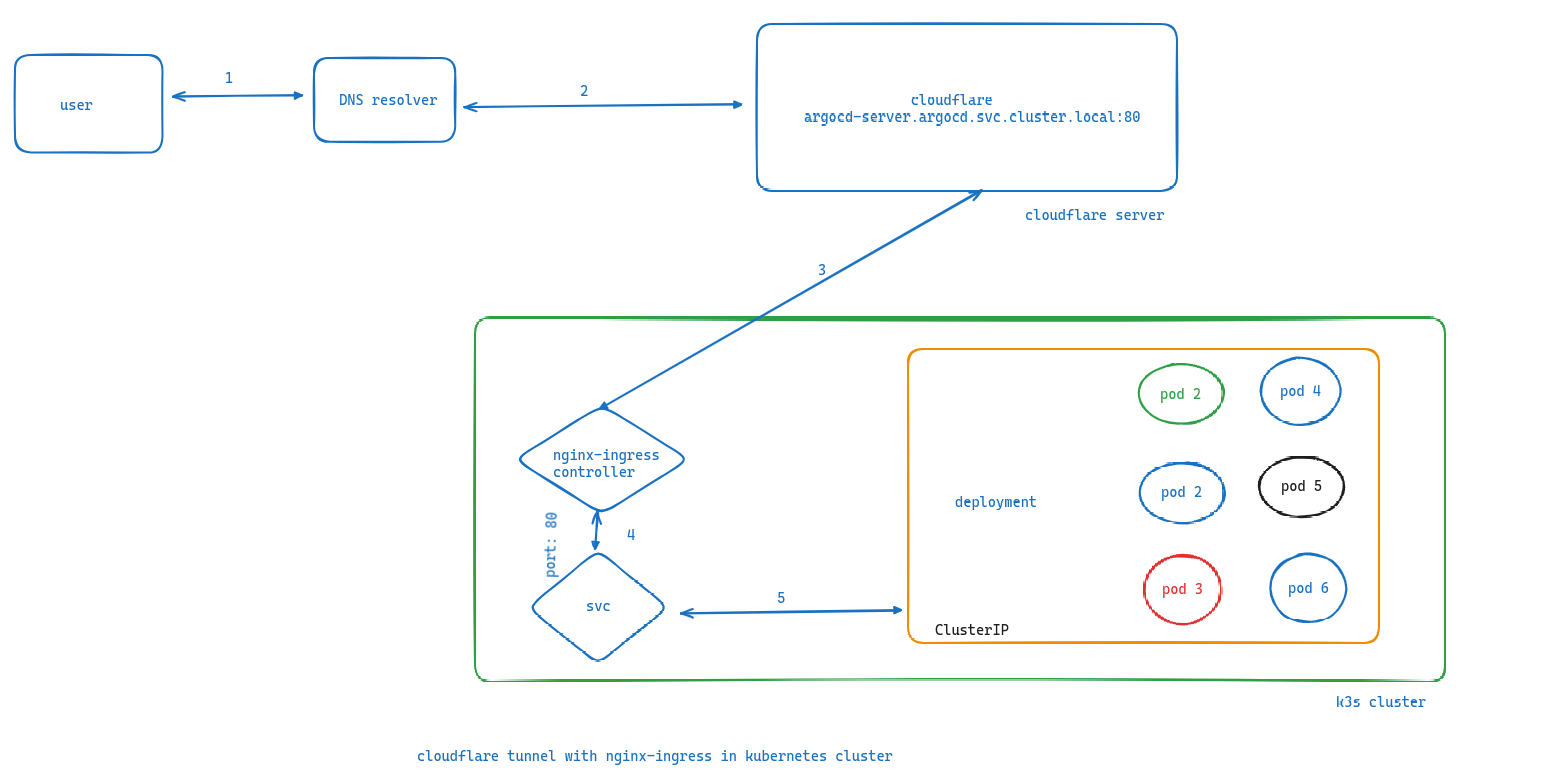
User initiates a request to a web application hosted on a cluster server. DNS resolution directs the user to Cloudflare. Cloudflare acts as a reverse proxy, terminating the SSL/TLS connection and initiating a tunnel to the Nginx ingress controller in the Kubernetes cluster. The Nginx ingress controller routes the request based on the Host header to the appropriate service within the cluster. The service distributes traffic across pods running the application. A selected pod processes the request and generates a response. The response travels back through the Nginx ingress controller, Cloudflare tunnel, and finally to the user’s device.
Install and configure argocd and nginx-ingress
First we have install argocd high availability version on our bare metal server. To install this,
sudo kubectl create namespace argocd
sudo kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/v2.10.1/manifests/ha/install.yaml
Download With Curl (argocd CLI)
wget https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/download/v2.10.1/argocd-linux-amd64
mv argocd-linux-amd64 argocd
chmod +x argocd
mv argocd /usr/local/bin/
Retrieve this password using the argocd CLI:
sudo kubectl -n argocd get secret
sudo kubectl -n argocd get secrets argocd-initial-admin-secret -o json
sudo kubectl -n argocd get secrets argocd-initial-admin-secret -o json | jq .data.password -r | base64 -d
To edit any service of argocd
sudo kubectl -n argocd edit svc argocd-server
Create argocd-ingress rule to route trafic
## argocd-ingress.yml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: argocd-ingress
namespace: argocd
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "false"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
spec:
rules:
- host: argocd.example.com
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: /
backend:
service:
name: argocd-server
port:
number: 80
Create argocd-tunnel for configure cloudflare
## argocd-tunnel.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
namespace: argocd
labels:
app: cloudflared-argocd
name: cloudflared-argocd
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: cloudflared-argocd
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cloudflared-argocd
spec:
containers:
- name: cloudflared-argocd
image: cloudflare/cloudflared:latest
# image: ghcr.io/maggie0002/cloudflared:2022.7.1
imagePullPolicy: Always
args:
[
"tunnel",
"--no-autoupdate",
"run",
"--token=place_your_token_here",
]
restartPolicy: Always
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 60
Configure nginx-ingress for handle ingress trafic
Link: https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.8.2/deploy/static/provider/baremetal/deploy.yaml
Modify the simply set server.insecure: "true" in the argocd-cmd-params-cm ConfigMap
sudo kubectl -n argocd edit configmap argocd-cmd-params-cm

Make sure to stop redirection http to https inside cloudflare
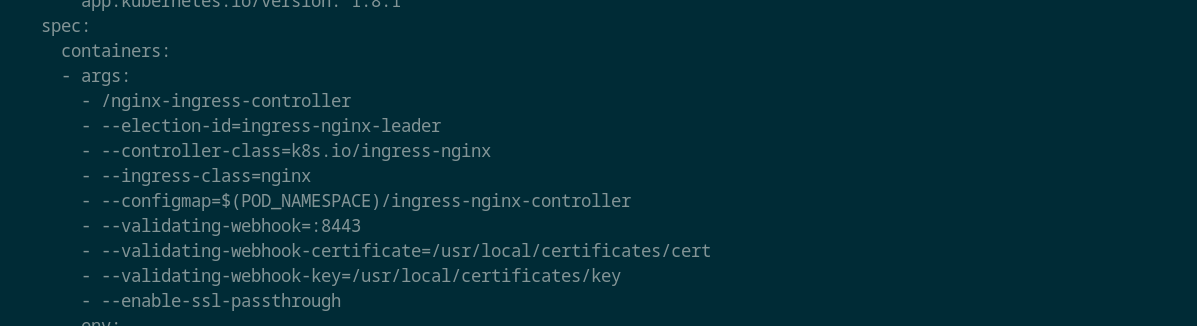
Next make the change in nginx ingress controller deployment to add the enable-ssl-passthrough flag as shown below
kubectl edit deploy ingress-nginx-controller -n ingress-nginx
Now its time to apply those two argocd-ingress.yml and argocd-tunnel.yml file
sudo kubectl apply -f argocd-ingress.yml
sudo kubectl apply -f argocd-tunnel.yml
To make everything work perfectly, roleout the core-dns from kube-system namespace and restart deployment from argocd namespace.
kubectl rollout restart deployment coredns -n kube-system
sudo kubectl rollout restart deployment --namespace=argocd
sudo kubectl rollout restart deployment --namespace=ingress-nginx
Operating procedure
Create Application
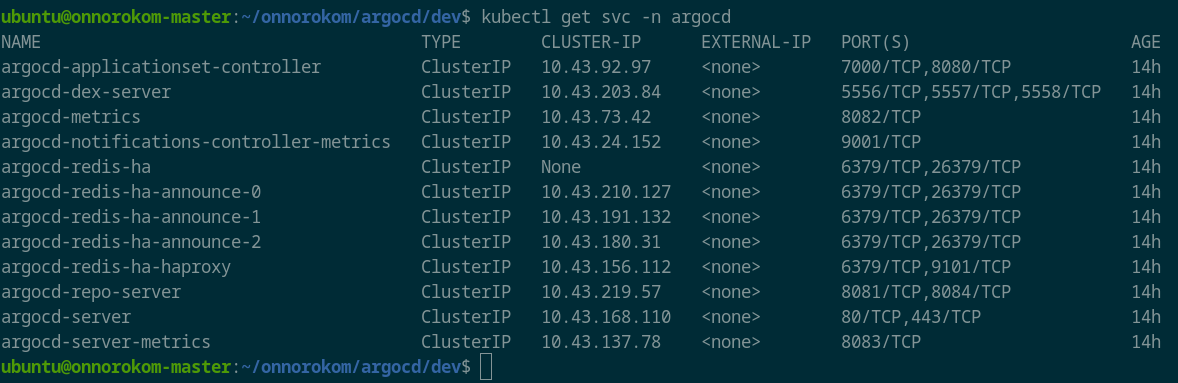
before creating application, you must login to the sysyem. first check the argocd-server svc ip, then
kubectl get svc -n argocd
Look for argocd-server ip
Login to argocd
argocd login 10.43.168.110
argocd app list
Create application (using cli)
argocd app create auth-api \
--repo https://net.osl.team:20613/m2saas/core/M2S.AuthAPI.git \
--path k8s/dev \
--dest-namespace default \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc \
--directory-recurse \
--sync-policy automated
sync application
argocd app sync auth-api
Check app logs
argocd app logs auth-service
Rollback with Argo CD CLI:
To rollback to a previous application revision, you can use the argocd app rollback command. You need to specify the name of the application and the target revision you want to roll back to.
argocd app rollback <APP_NAME> --revision <REVISION_NUMBER>
<APP_NAME>is the name of the application you want to rollback.<REVISION_NUMBER>is the target revision number you want to roll back to. You can obtain revision numbers usingargocd app history <APP_NAME>.
For example:
argocd app rollback auth-api --revision 3
Rollout with Argo CD CLI:
To trigger a manual rollout of an application in Argo CD, you can use the argocd app sync command. This command synchronizes the application state with the desired state defined in the Git repository.
argocd app sync <APP_NAME>
<APP_NAME>is the name of the application you want to trigger a rollout for.
For example:
argocd app sync auth-api
if needed,
kubectl rollout restart deployment coredns -n kube-system
sudo kubectl rollout restart deployment --namespace=argocd
For your information, to delete CDR and argocd app-
Delete CRDs
sudo kubectl patch crd applications.argoproj.io -p '{"metadata": {"finalizers": null}}' --type merge
sudo kubectl delete crd applications.argoproj.io
Delete argocd apps
sudo kubectl patch app auth-api-test -p '{"metadata": {"finalizers": null}}' --type merge
sudo kubectl delete app auth-api
Thanks for your read.
Happy Coding.